A muscle tear in the leg is a common injury that often occurs in connection with sports, exercise, or contact sports. The injury is caused by the tearing of muscle tissue, which leads to bleeding, swelling, and pain.
What is a muscle tear?
A muscle tear is a partial or complete tear of muscle tissue, often at the junction between muscle and tendon. The injury can be a small tear or a complete rupture. The most common areas are the thigh muscles and calf muscles, but tears can occur in all muscle groups. The risk increases with poor warm-up, previous injuries, age, or cold and tight muscles.
Common causes & risk factors
Muscle tears often occur with explosive movements, incorrect loading or direct force as in contact sports. Overexertion with high training volume, insufficient warm-up and scar tissue from previous injuries also increase the risk. Cold and tight muscles reduce elasticity and make the muscle more vulnerable.
Symptom
-
Sudden stabbing pain in the muscle at the time of injury
-
Local swelling, warmth, and redness over the injured area
-
Bluish discoloration due to bleeding
-
Pain with movement and sometimes even at rest
-
Impaired function and strength in the affected muscle
When should you seek medical attention?
If the pain is severe, persists for more than 24 hours, or if you experience significant functional impairment, you should contact your healthcare provider. An extensive rupture may require medical examination to rule out secondary injuries.
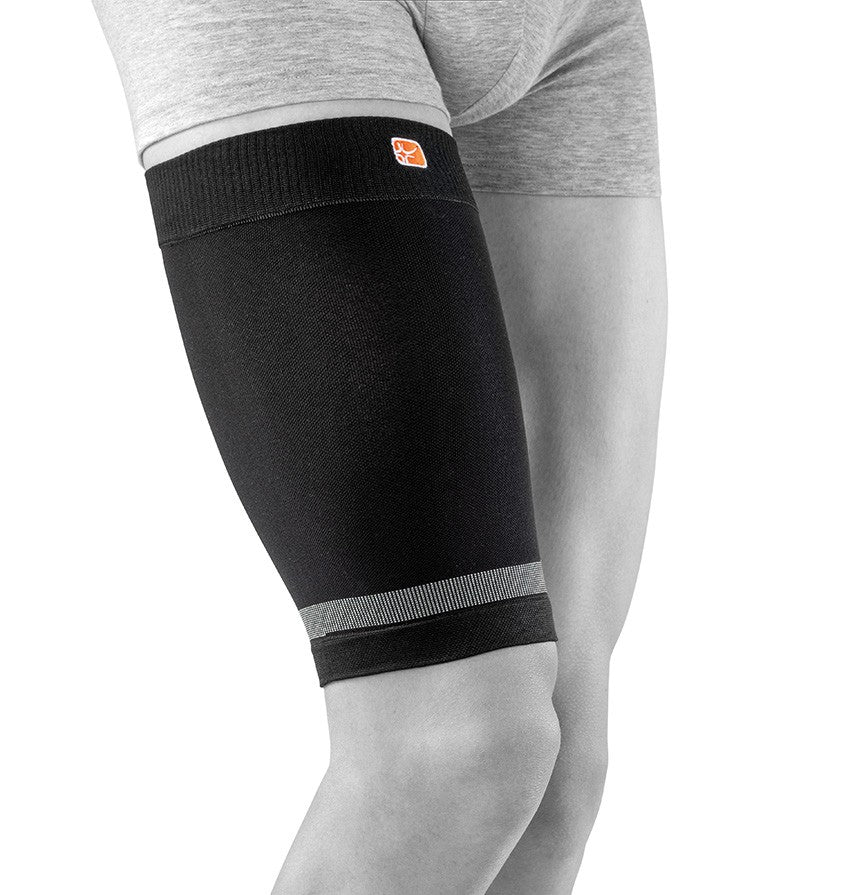
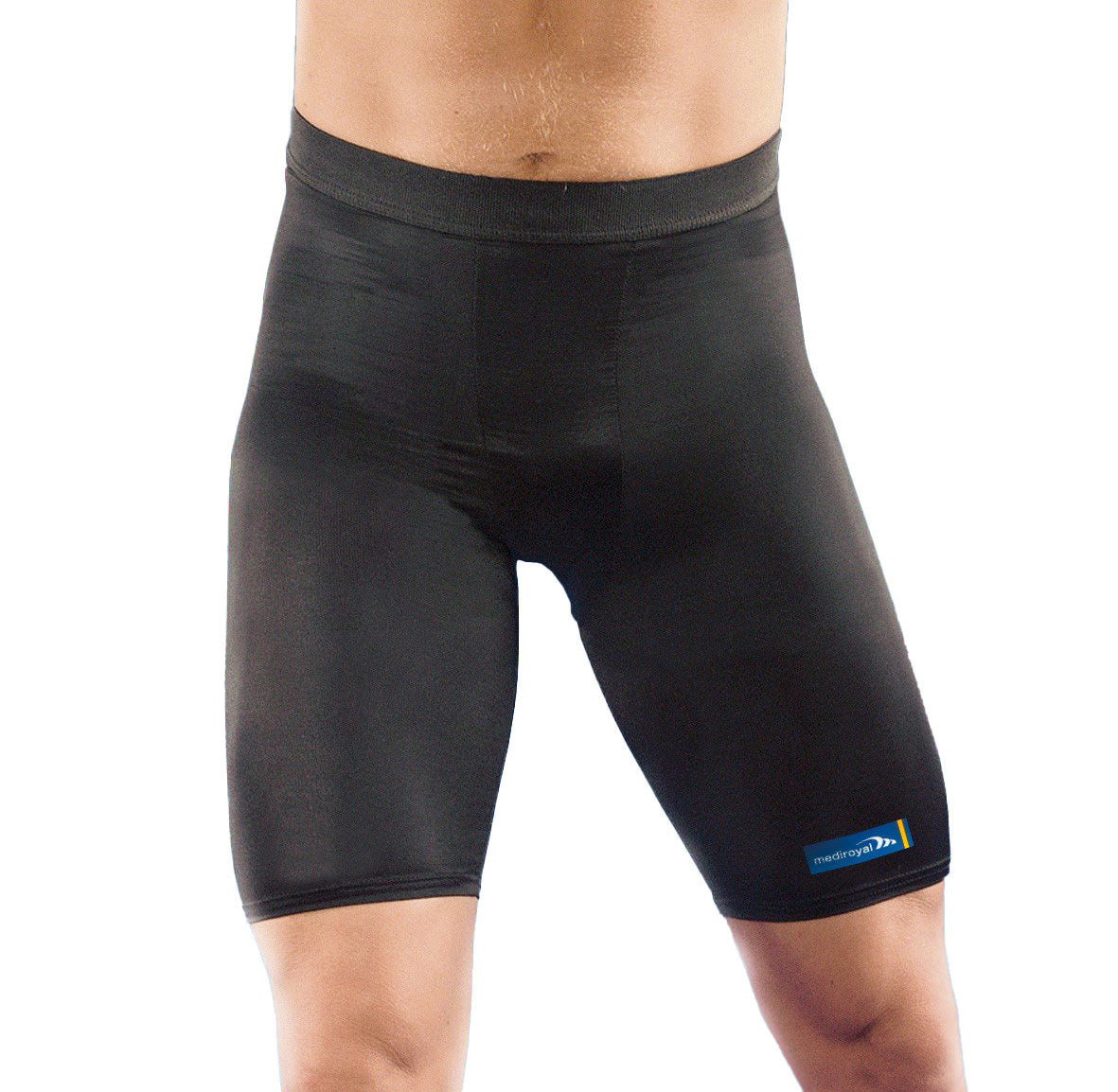
Recommended protection & support
In the case of a muscle tear, rapid compression and cold immediately after the injury are crucial to reduce bleeding and swelling. Compression bandages or special protection for the thigh or calf are effective in providing pressure and stability. The combination of compression, cold and elevation (PRICE principle) is a proven emergency measure. Once the acute phase has subsided, a compression support can be used during activity to improve circulation and reduce the risk of recurrence. Regular stretching and rehabilitation training in consultation with a physiotherapist is important to regain strength and prevent new injuries.