Wrist pain – causes, symptoms and wrist support
Wrist pain is a common problem that can affect both athletes and people with sedentary jobs. The pain is often due to overuse, but can also be caused by osteoarthritis, inflammation, or reduced stability.
What is wrist pain?
The wrist is exposed to heavy strain every day – from computer work to heavy manual work. Overuse of muscles, tendons and ligaments is the most common cause of pain, but wear and tear (arthritis) and local inflammation can also cause discomfort. Instability in the wrist after injury is another cause that can lead to recurring pain.
Common causes & risk factors
Wrist pain often develops due to one-sided movements and repetitive strain, for example when working on a computer or using tools. Osteoarthritis with worn-out articular cartilage can lead to stiffness and swelling, while local inflammation in muscles, tendons or ligaments can also be behind the discomfort. Reduced stability after previous injuries or impact on the ligaments is another common cause that can make the wrist more sensitive to overload.
Symptoms
- Pain with movement or strain
- Stiffness and reduced mobility
- Local swelling around the wrist
- Instability and feeling of weakness in the grip
When should you seek medical attention?
Contact your healthcare provider if you have persistent pain that does not improve with rest, if swelling increases, or if you suspect ligament damage or fracture.
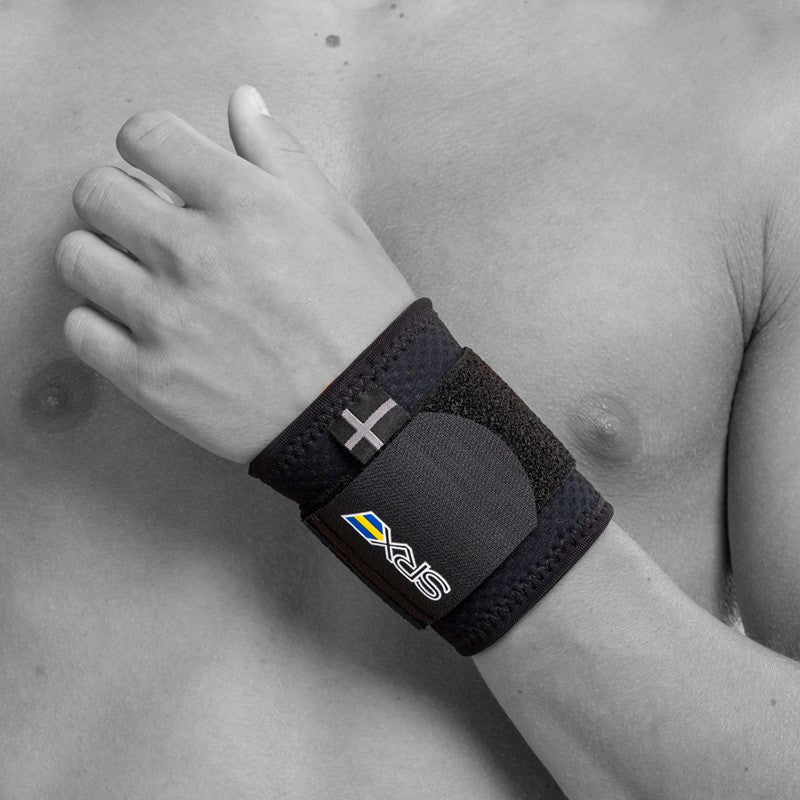
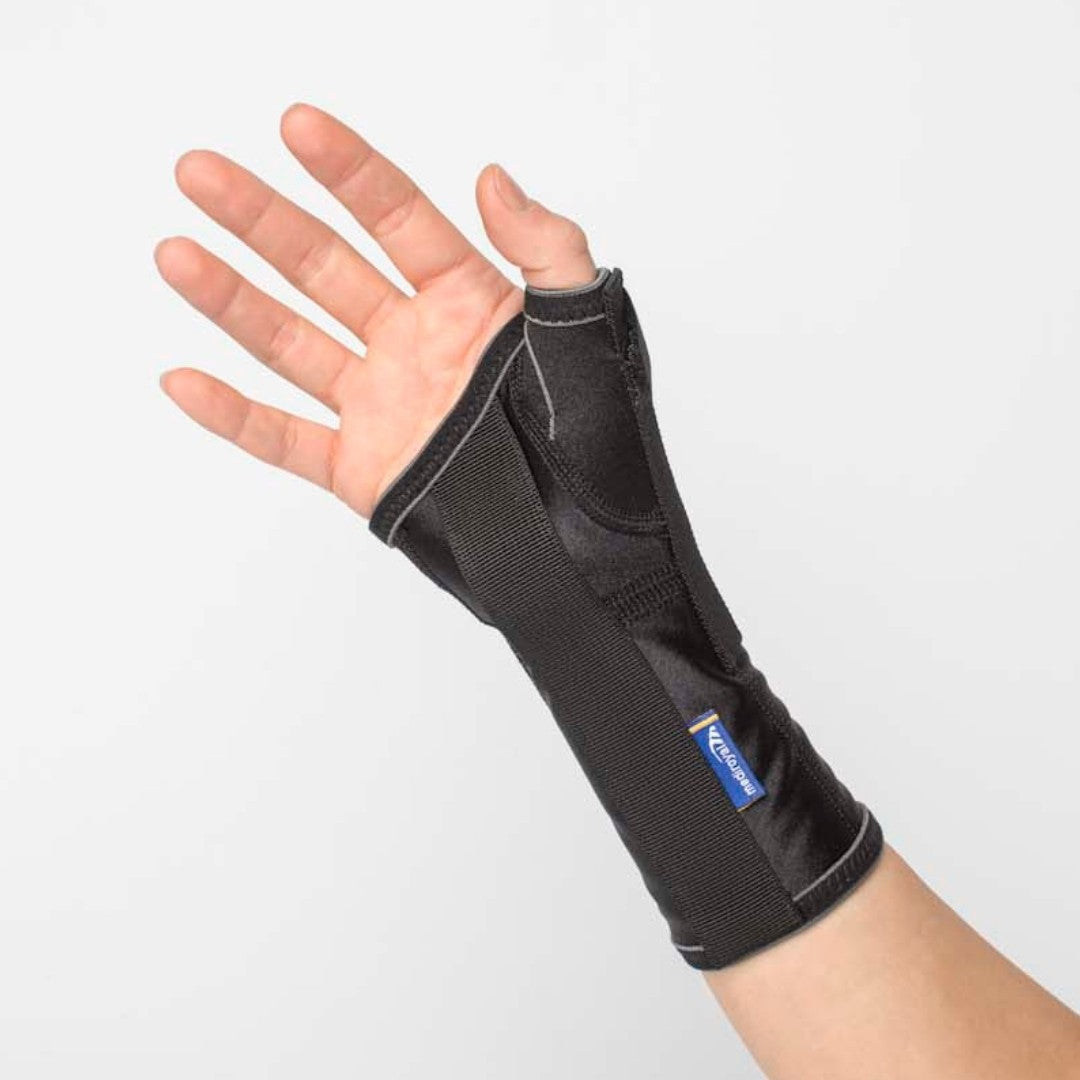
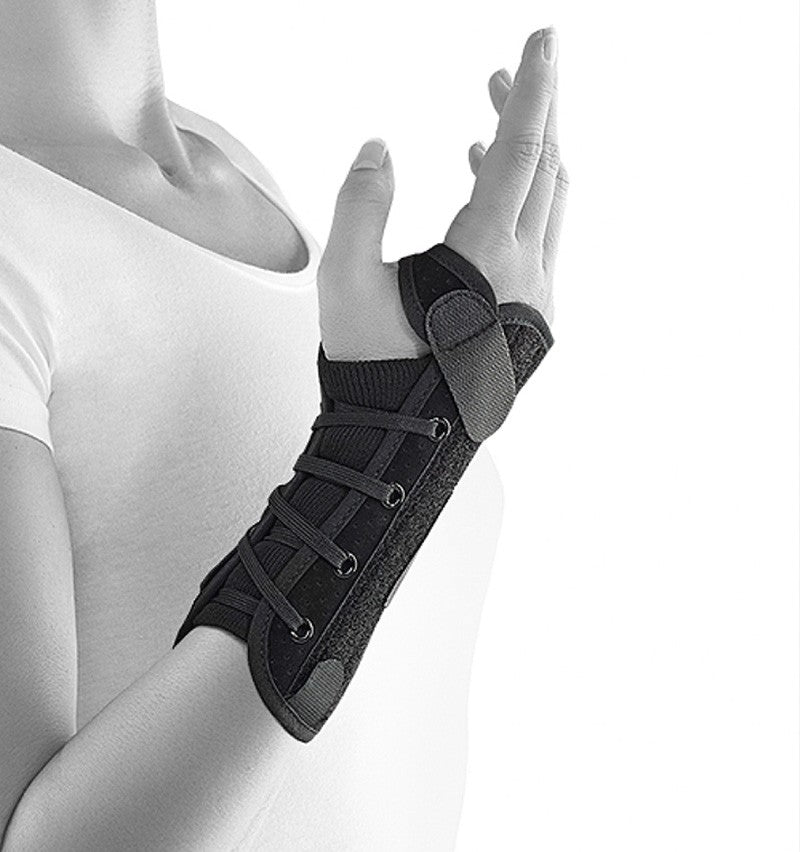
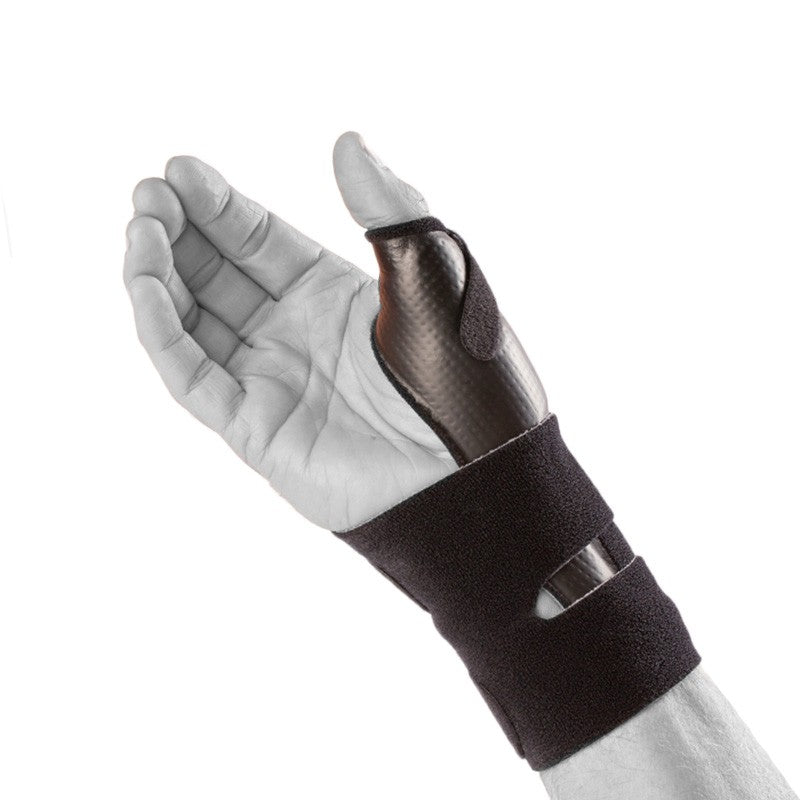
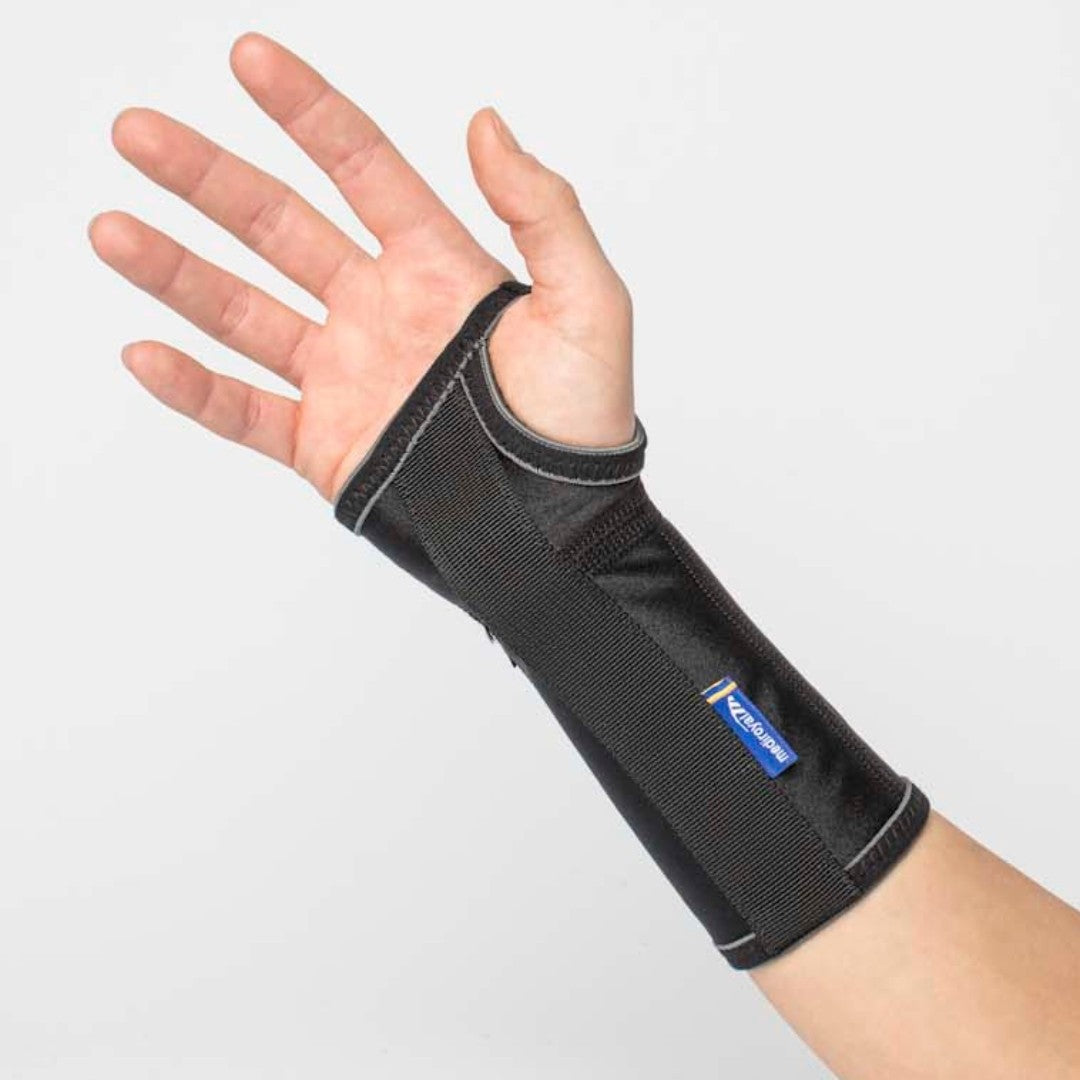
Recommended protection & support
If you have problems with your wrist, different types of protection and support can make everyday life easier. A wrist support with compression relieves and stabilizes when overloaded, while relieving protection can reduce pain in osteoarthritis or inflammation. For those with an unstable wrist after injury or ligament damage, a more stabilising support can provide extra security. Ergonomic aids, for example, for working at a computer or other repetitive tasks, also help to reduce strain and prevent further problems. See all our products for the hand, wrist and thumb here .
About our Injury Guide – quick guidance in case of complaints
In our Injury Guide, you will receive clear and easy-to-understand information about common injuries, how they occur and what symptoms usually occur. You will also receive recommendations on which protection and aids can relieve your discomfort and help you further in your rehabilitation. All information is based on expert knowledge from our licensed physiotherapist.
For more information about the hand and wrist, you can read more in the Injury Guide Hand & Wrist. You can also go to the Injury Guide's main page to read about other injuries and symptoms.
Related injuries:
- Thumb pain
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Inflammation of the wrist
- Thumb osteoarthritis (arthritis of the thumb)
Find the right protection for your needs
There are several ways to find the right product on our website. For a more personalised selection, you can use our filters and sort by injury, body part or sport. You can also get help from our AI assistant Eir, who is trained on all the content on our website and can help you with product recommendations, fit questions and order-related concerns – 24/7. If you would rather speak directly to our licensed physiotherapist, Ida, you can reach her via email or phone for personal advice and support in your product selection.